Types and Techniques of Lighting
Direction and Position of Light
The most basic element that determines the three-dimensionality of the subject.
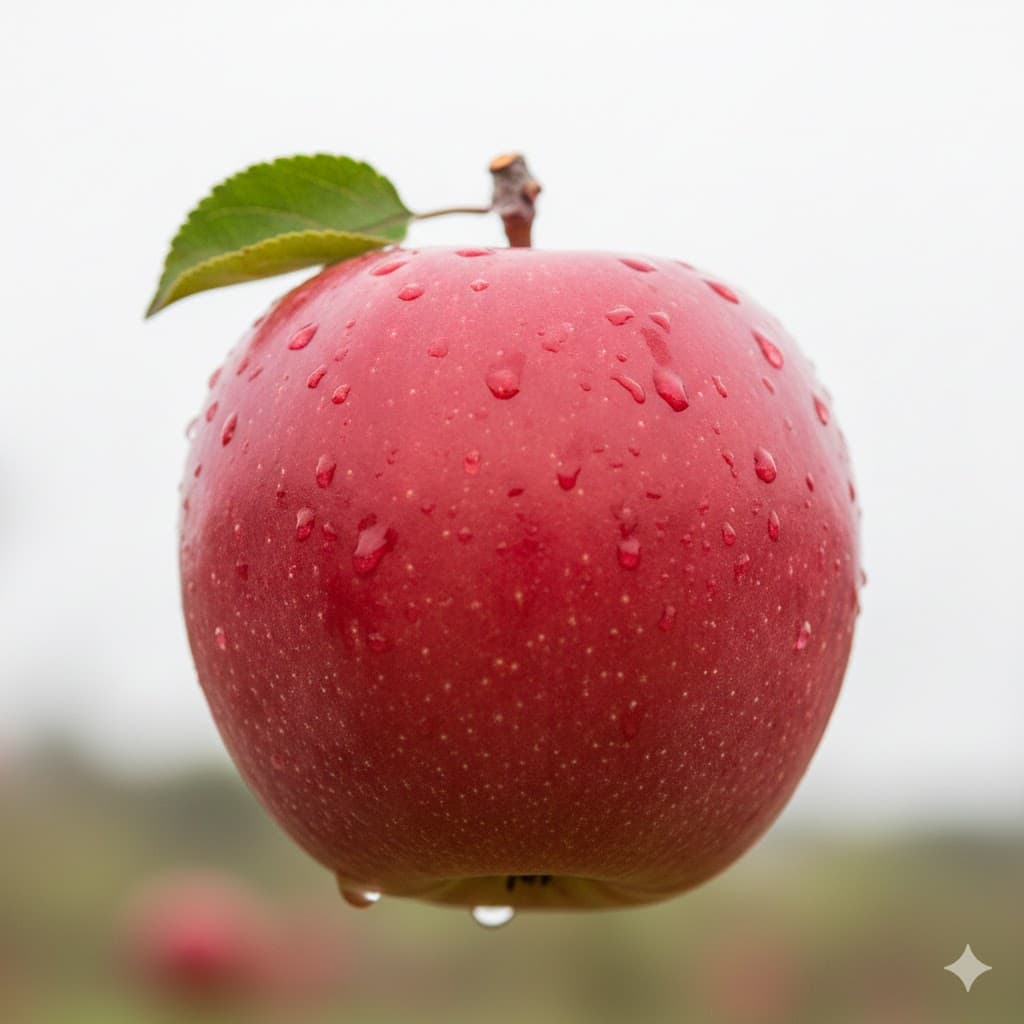

Front light, shining from the front of the subject, almost no shadows so it looks flat but details are clearly visible
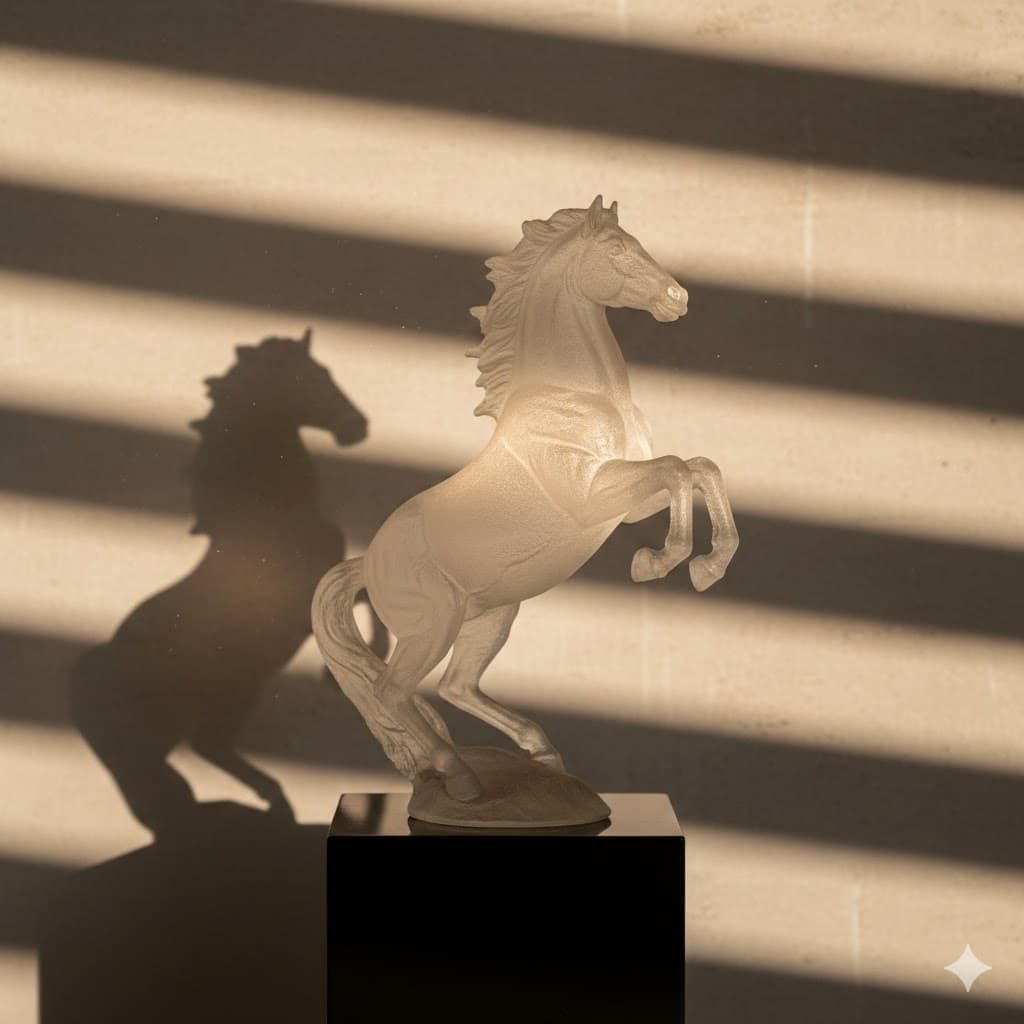

Side light, shining from the side, maximizes texture and three-dimensionality, suitable for dramatic portraits/landscapes
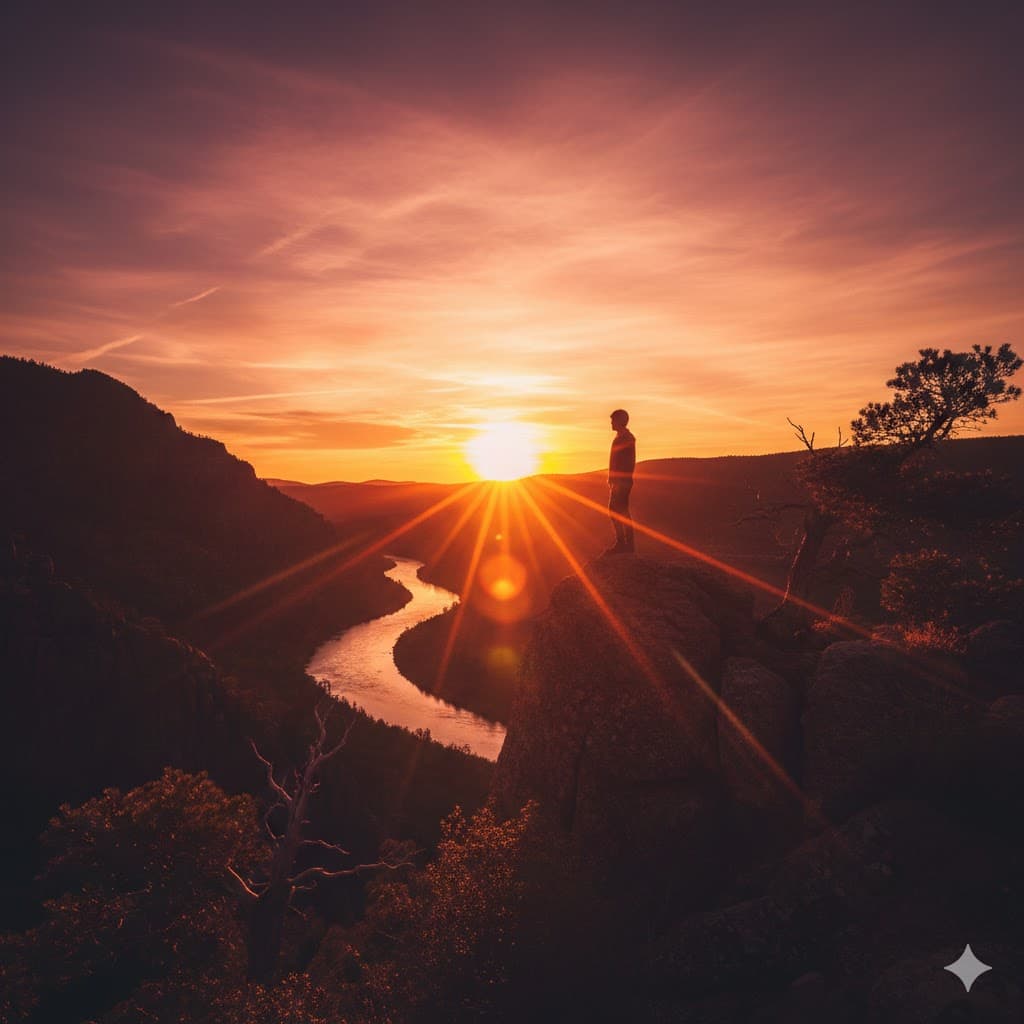

Backlight, shining from behind the subject, the person’s expression becomes dark but the silhouette and lines are emphasized
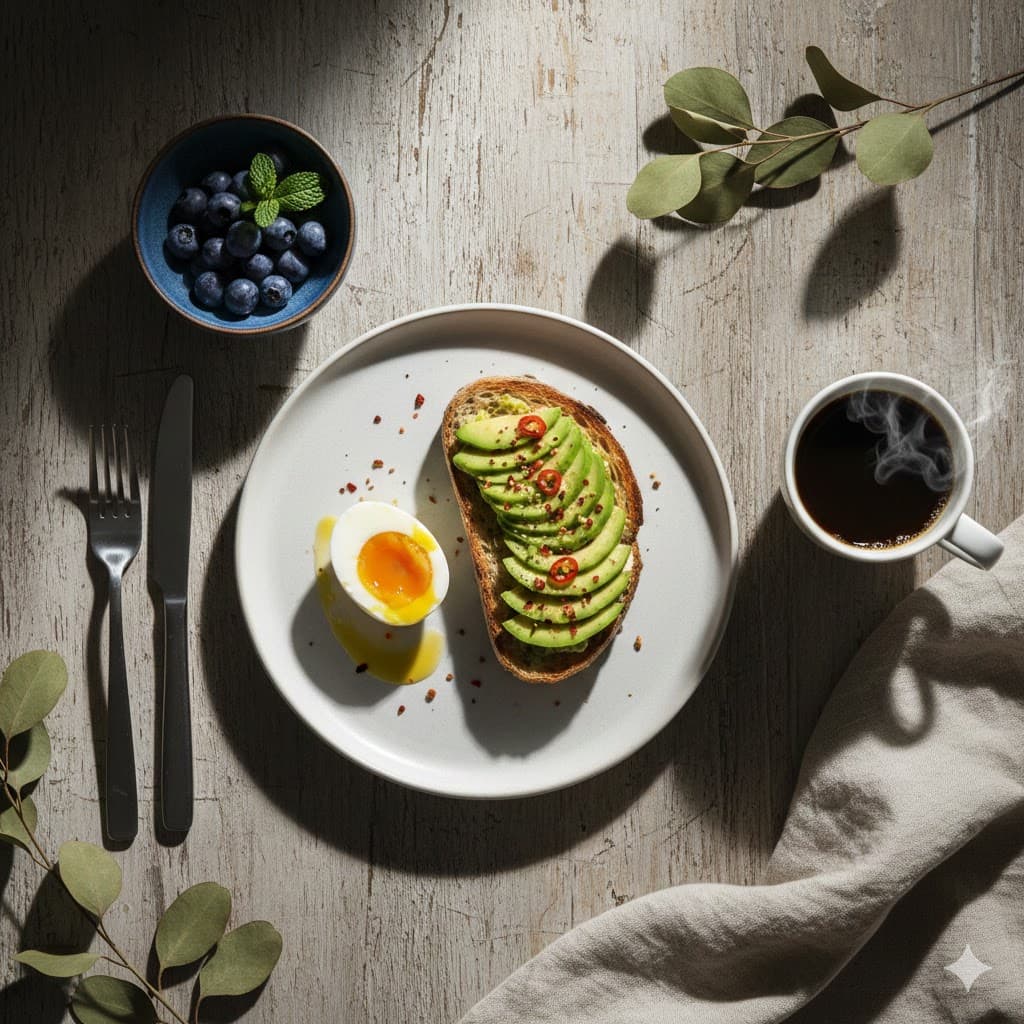

Top lighting, shining from above the head, gives a sublime or isolated feeling, casts shadows around the eyes
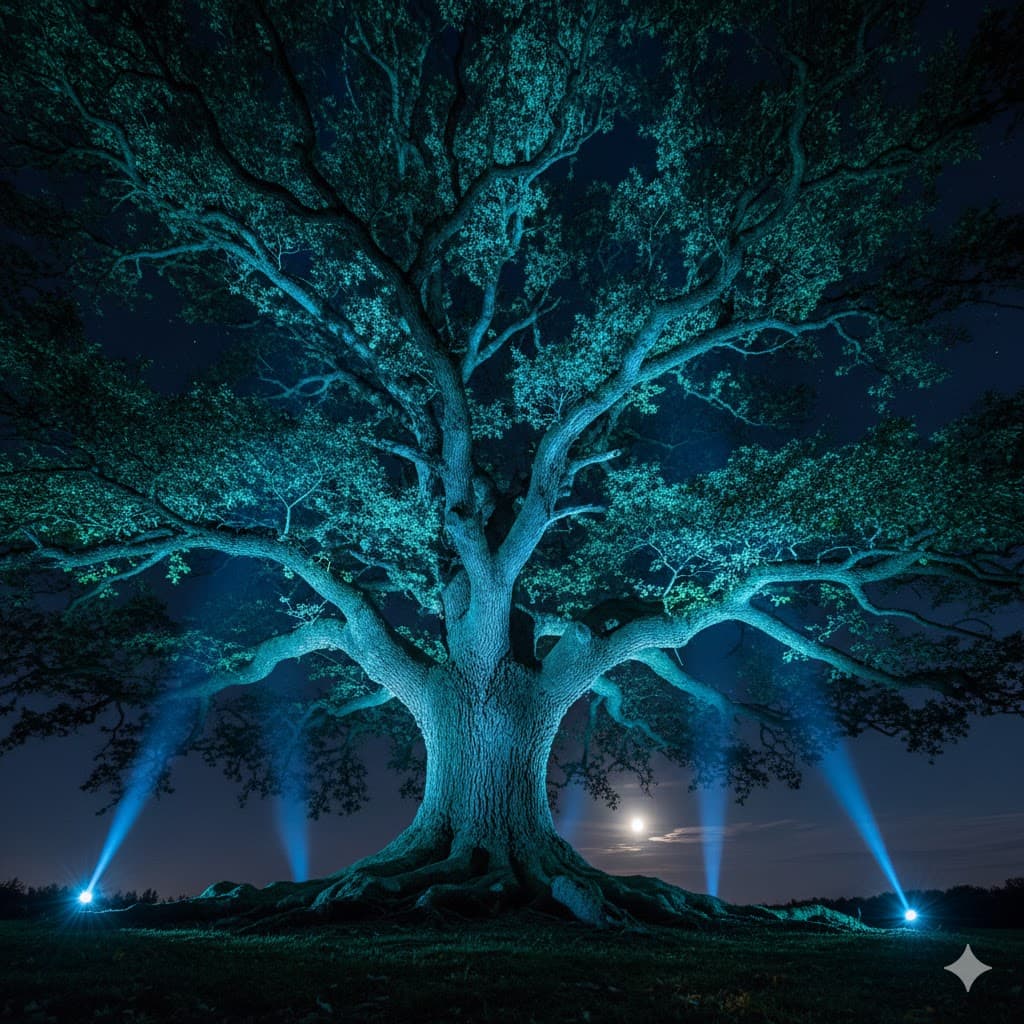

Uplighting, shining from below to above, creates a bizarre or intimidating atmosphere like a horror movie
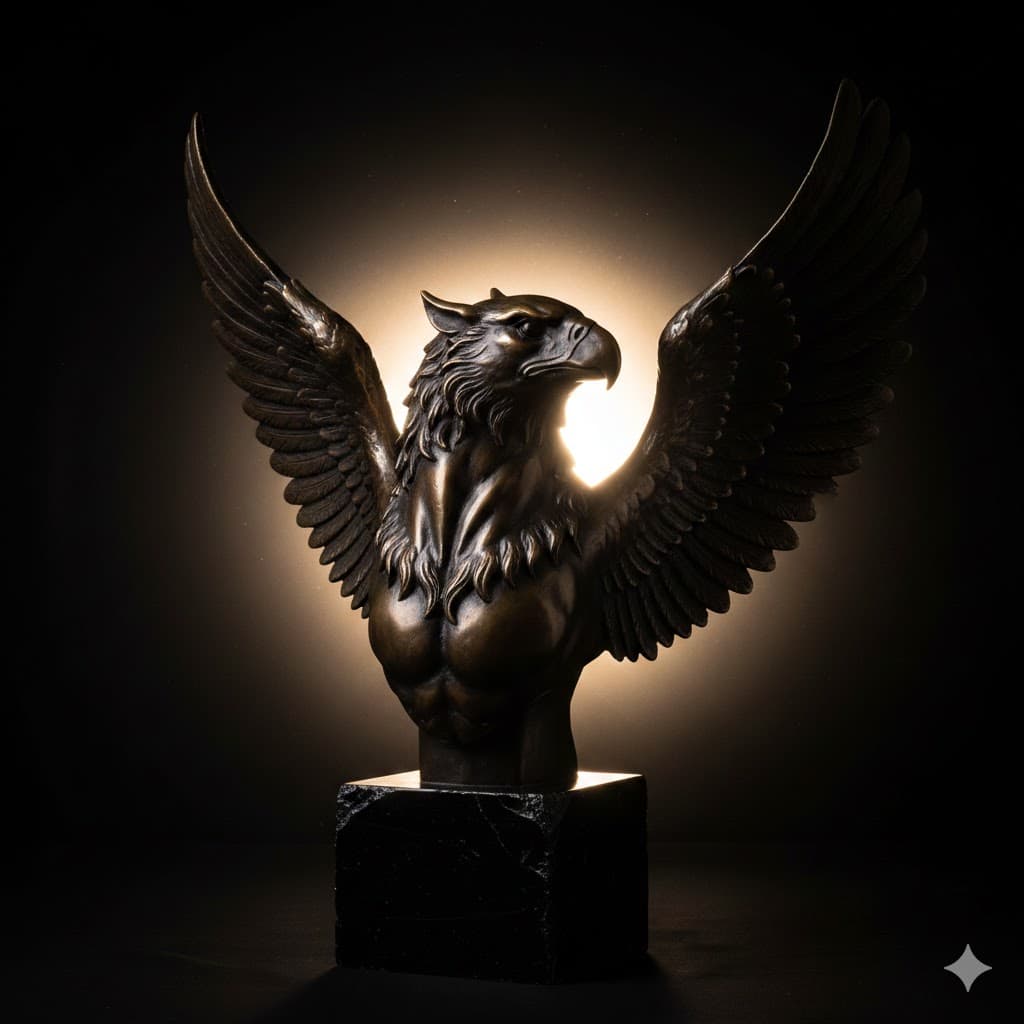

Rim light, shining diagonally from behind to create a band of light along the subject’s edges, essential for separating the subject from the background
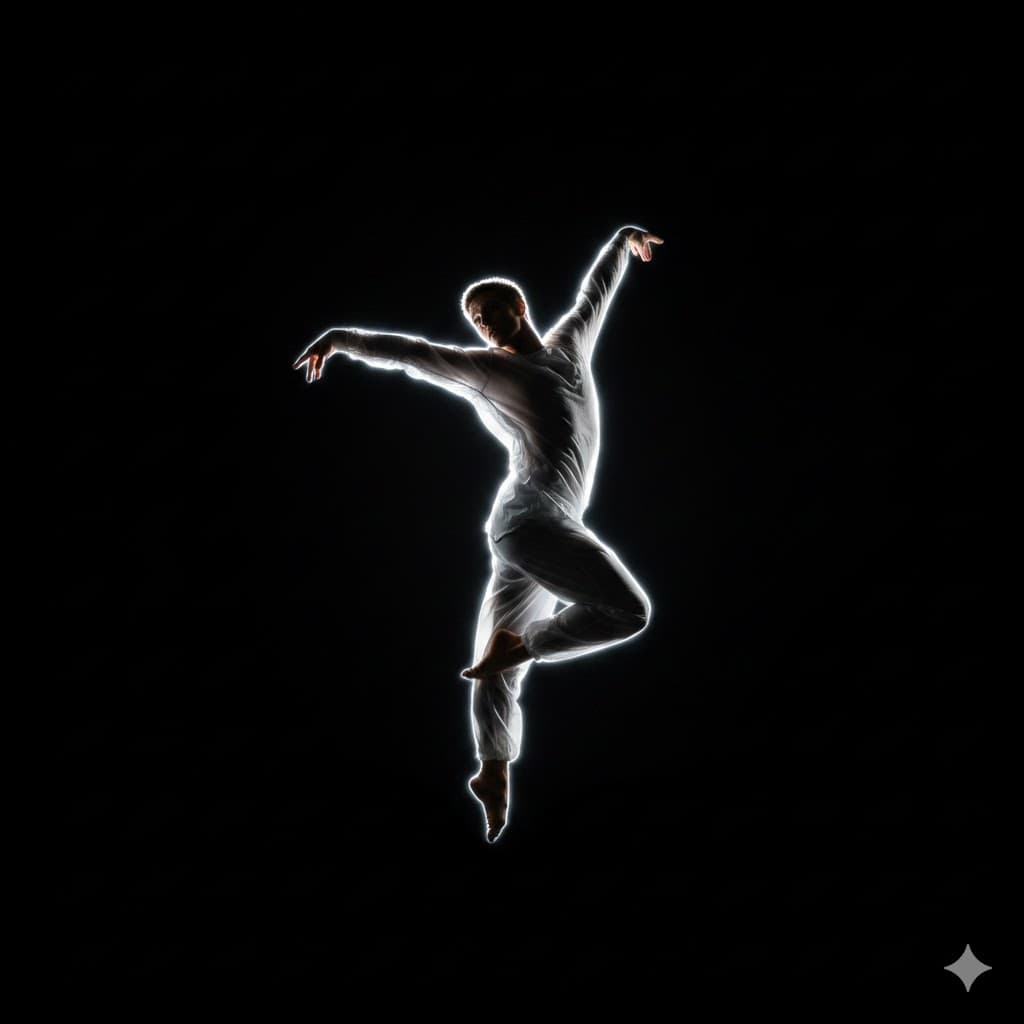

Kicker, similar to rim light but shining a bit more from the side to emphasize the contours of the cheek or shoulder
Texture and Contrast of Light
Controls the density and edges of shadows.
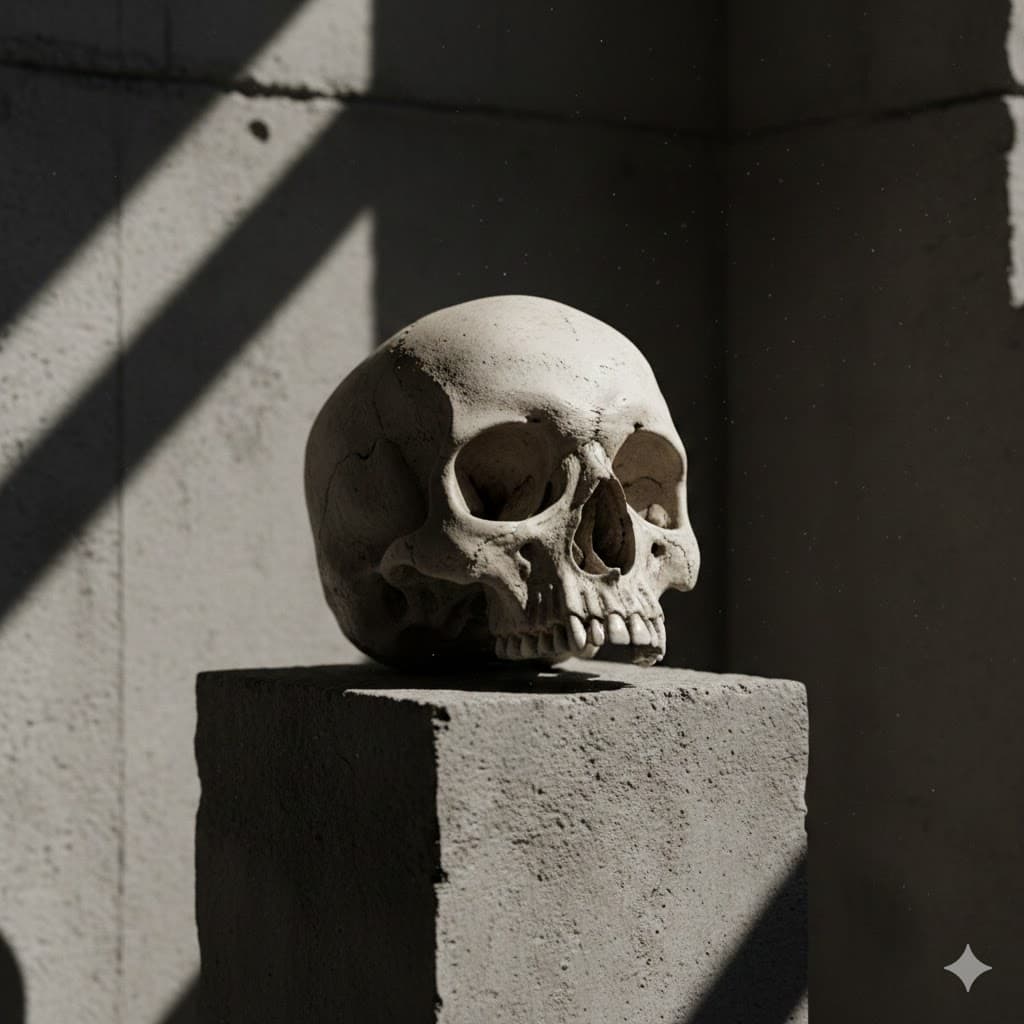

Hard lighting, small and strong light source, razor-sharp shadow edges and strong contrast, intense masculinity or noir
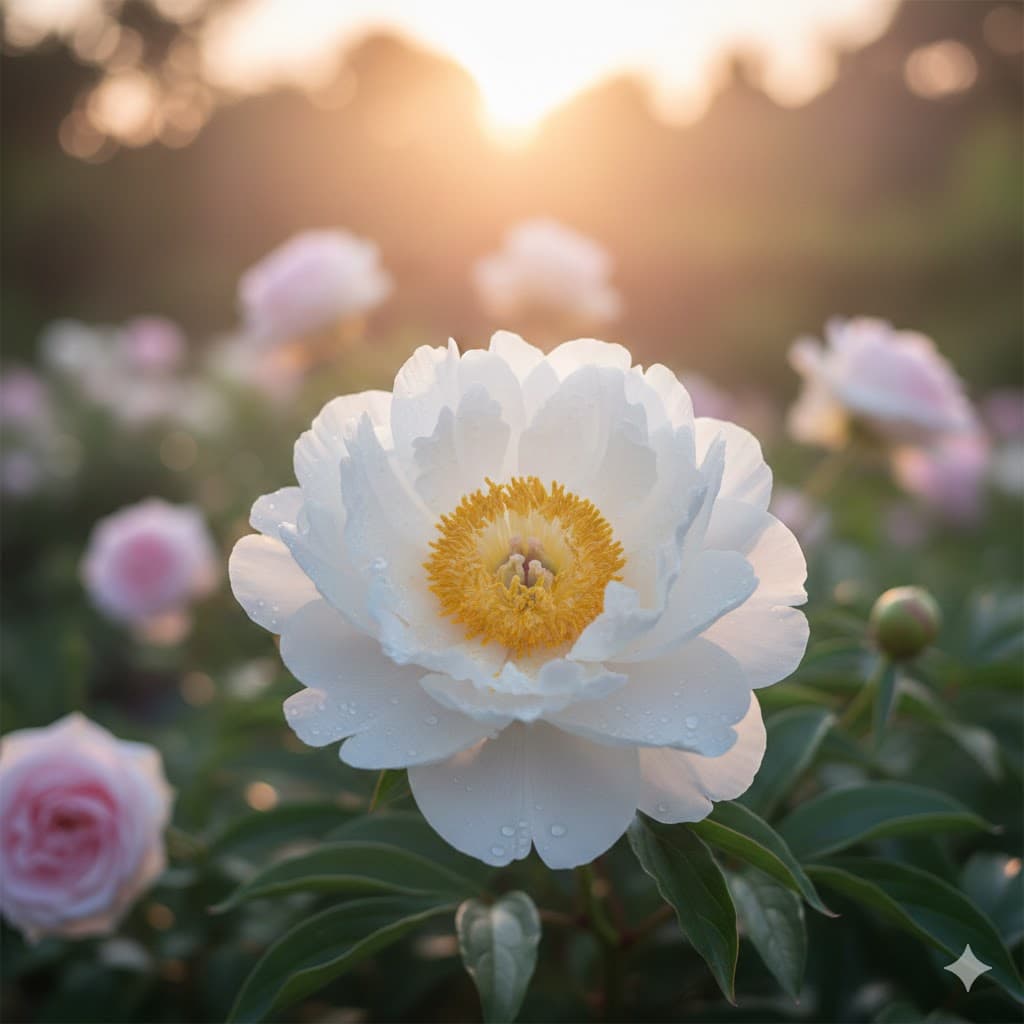

Soft lighting, large and diffused light source, shadows spread softly, used in beauty editorials or baby photos
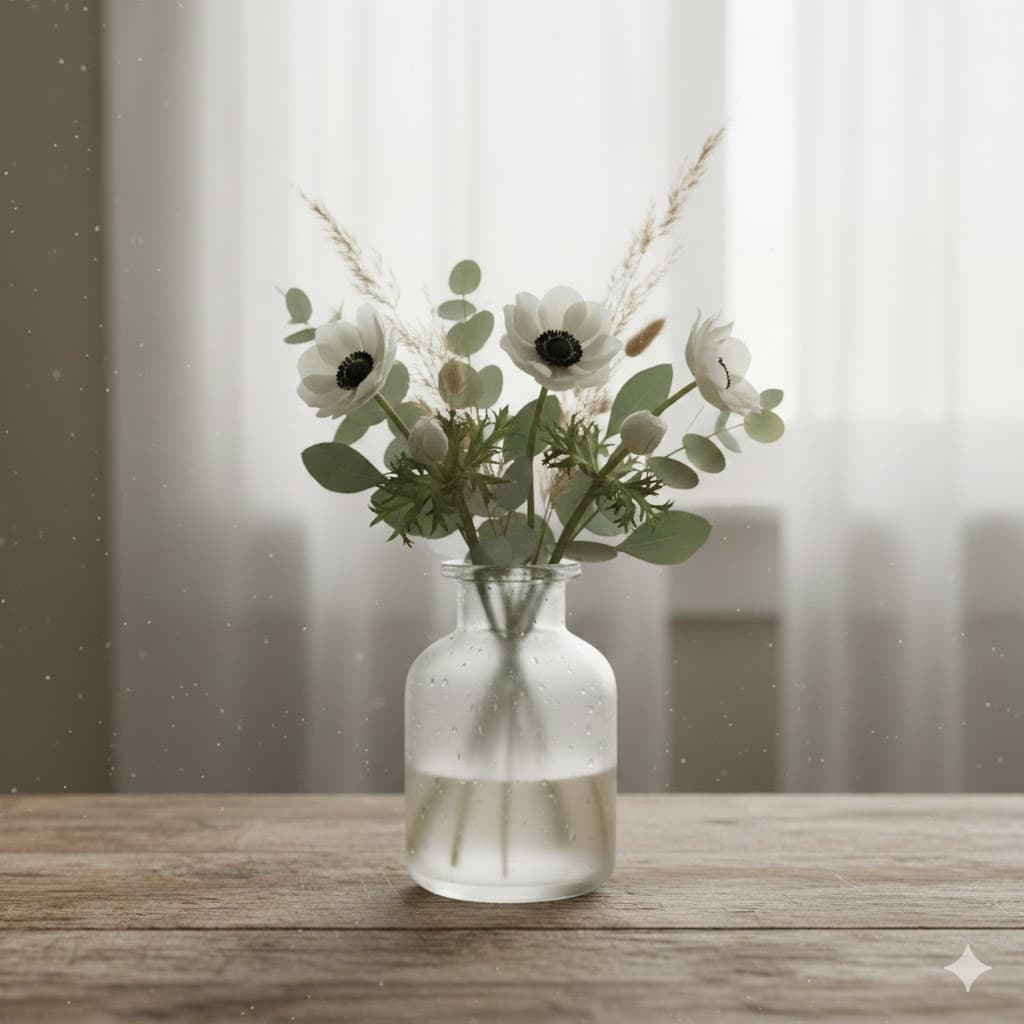

Diffused light, like light passing through clouds or curtains, spreads gently overall with no glare
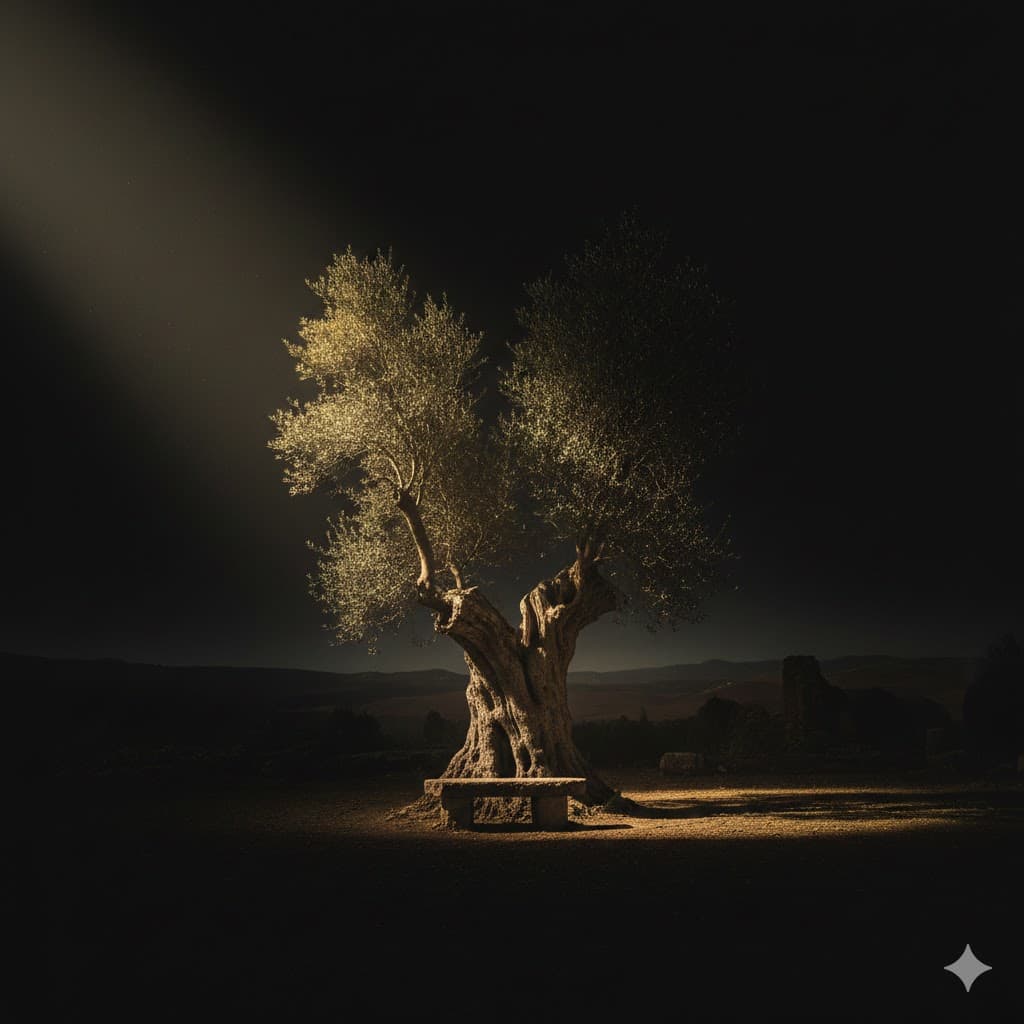

Chiaroscuro, a Baroque painting style that dramatically emphasizes the contrast between light and dark
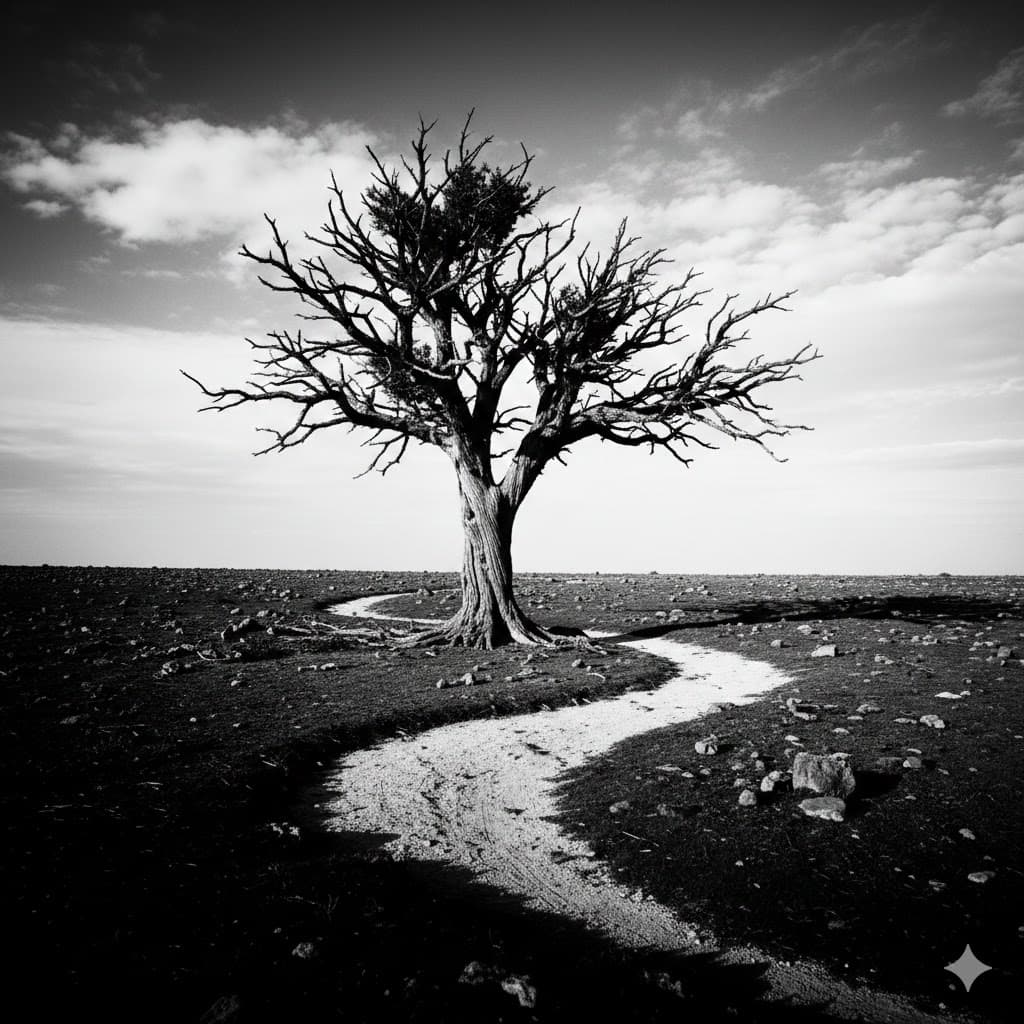

High contrast, very bright highlights and very dark shadows, leaves a strong impression
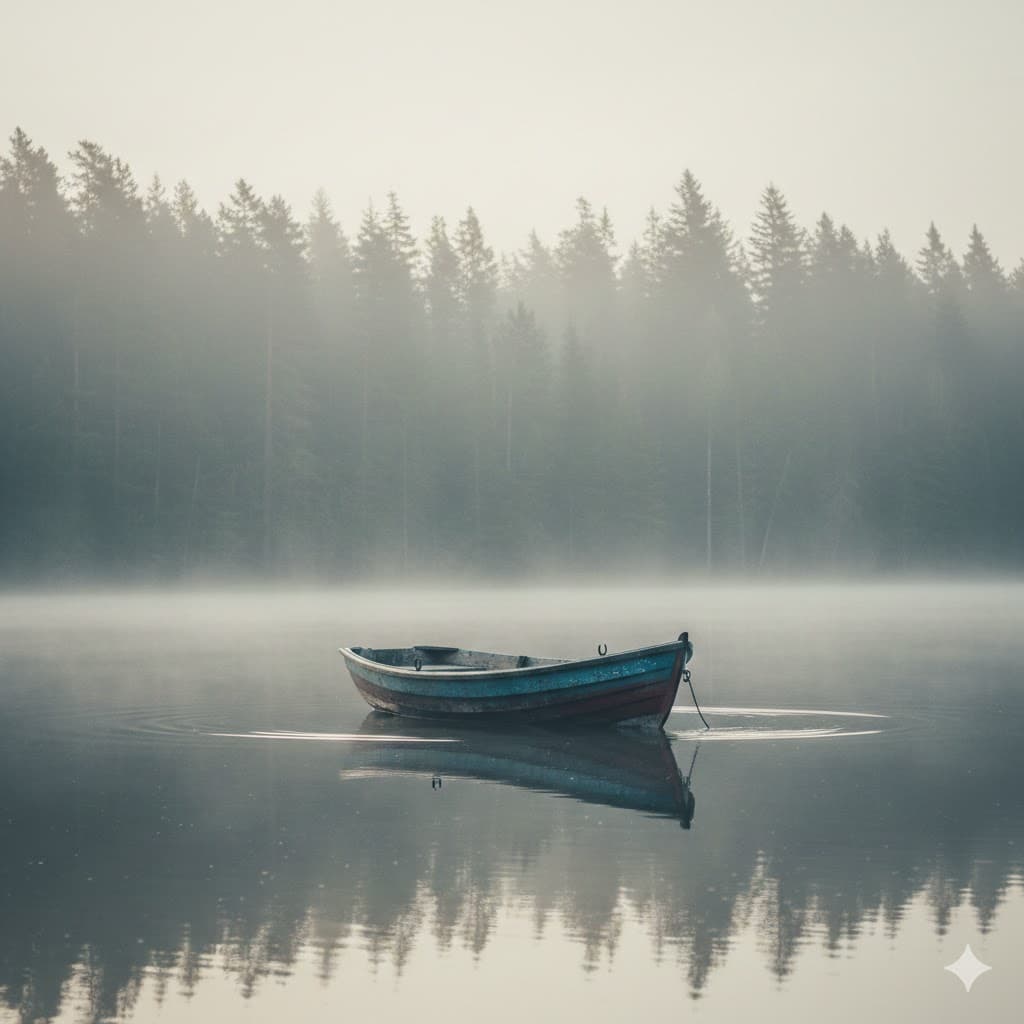

Low contrast, little difference between light and dark, giving a calm and vintage feel
Studio and Portrait Lighting Setups
Standardized lighting arrangements used by professional photographers in studios.
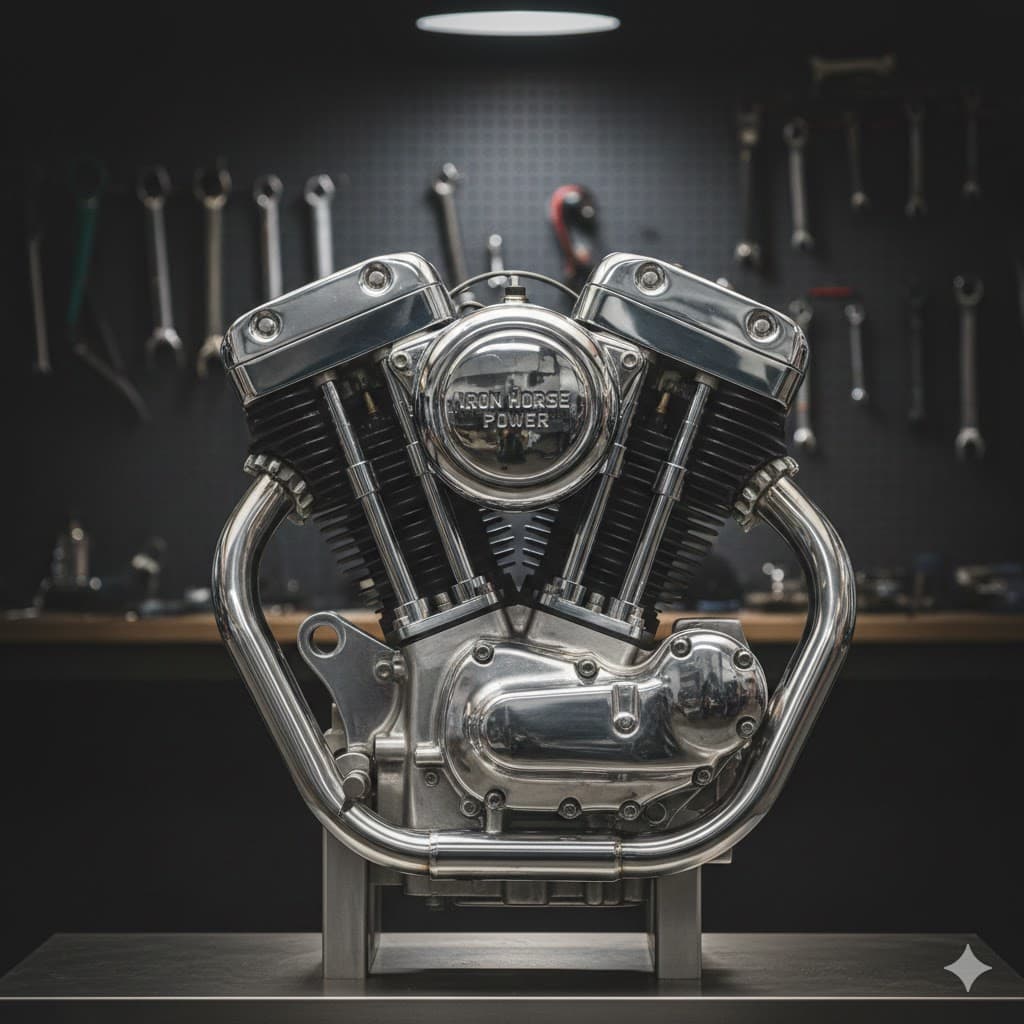

Three-point lighting, the most stable and three-dimensional 3D/broadcast standard lighting using key light + fill light + backlight
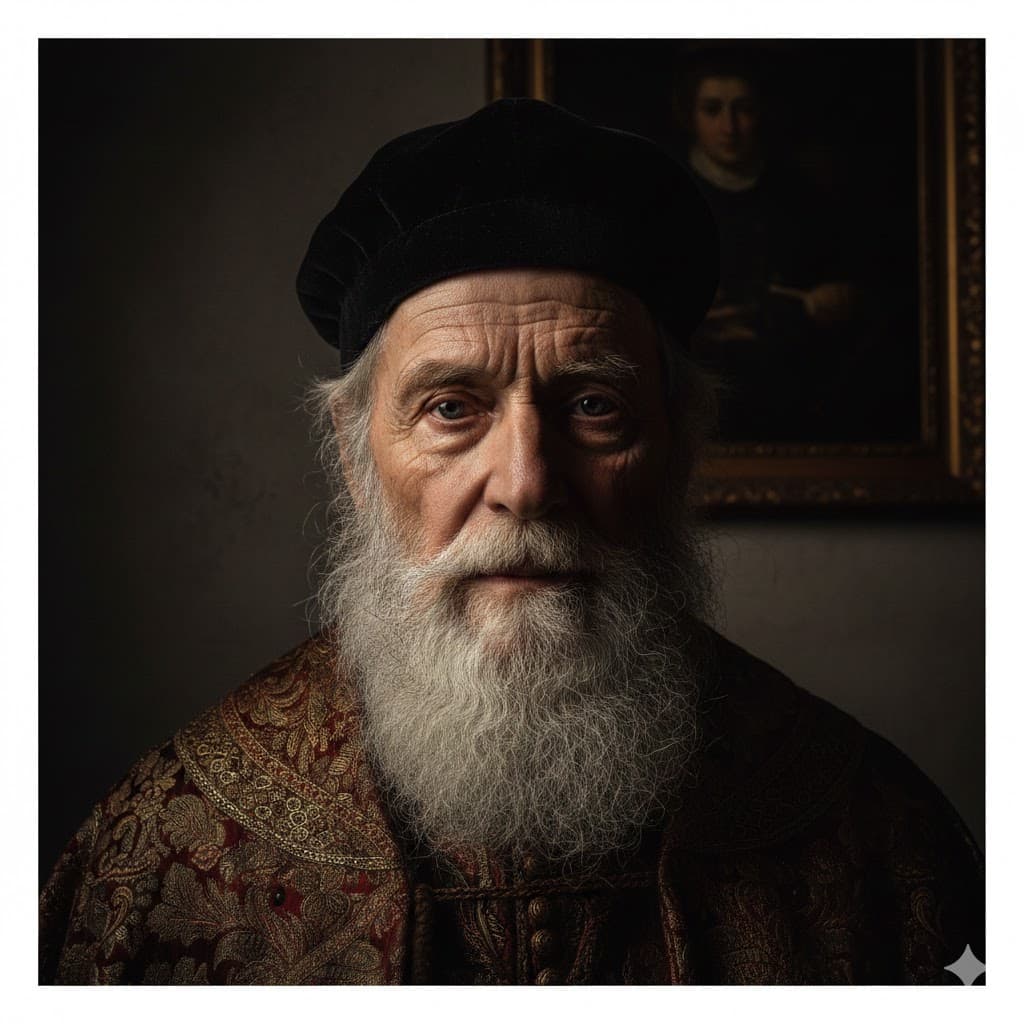

Rembrandt lighting, a classic and atmospheric technique that creates an inverted triangle of light on the cheek on the shadow side
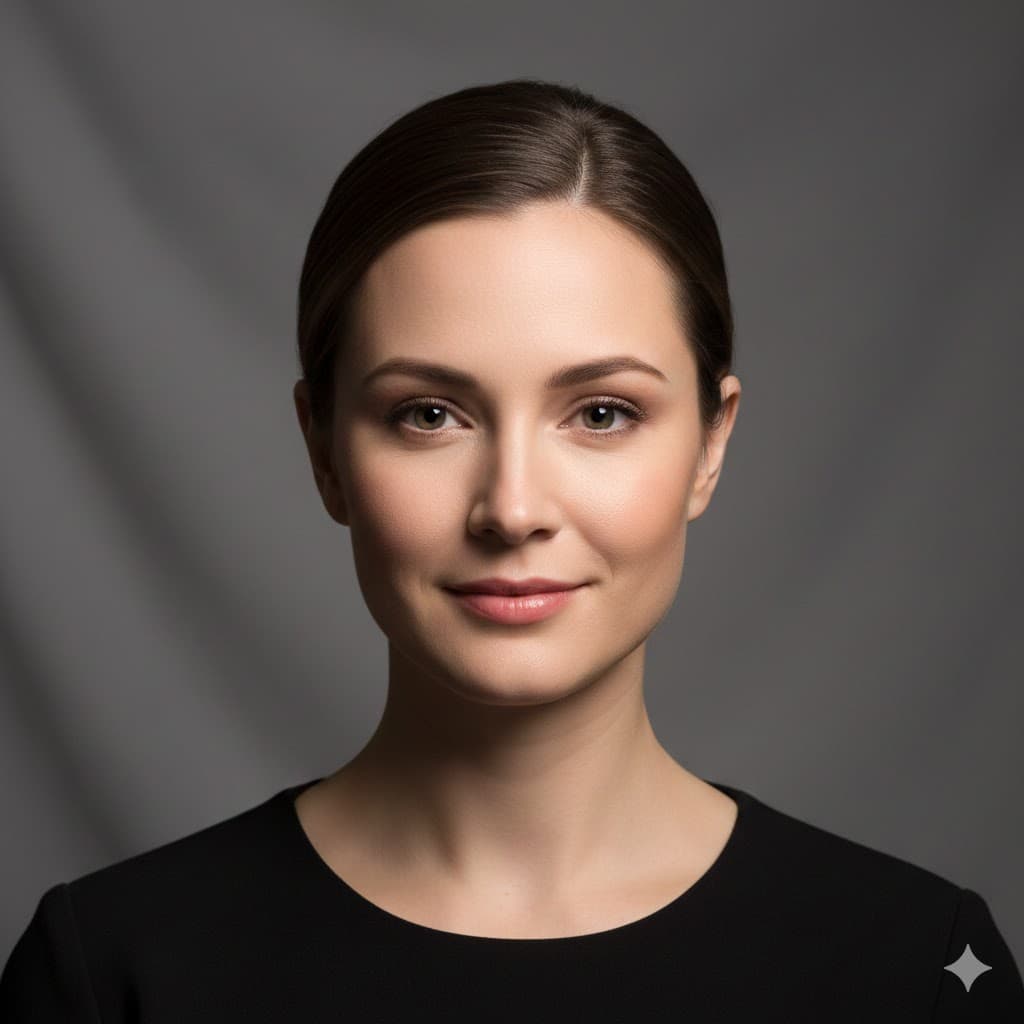

Butterfly lighting, shining from above and in front to create a butterfly-shaped shadow under the nose, makes the face look slimmer and glamorous
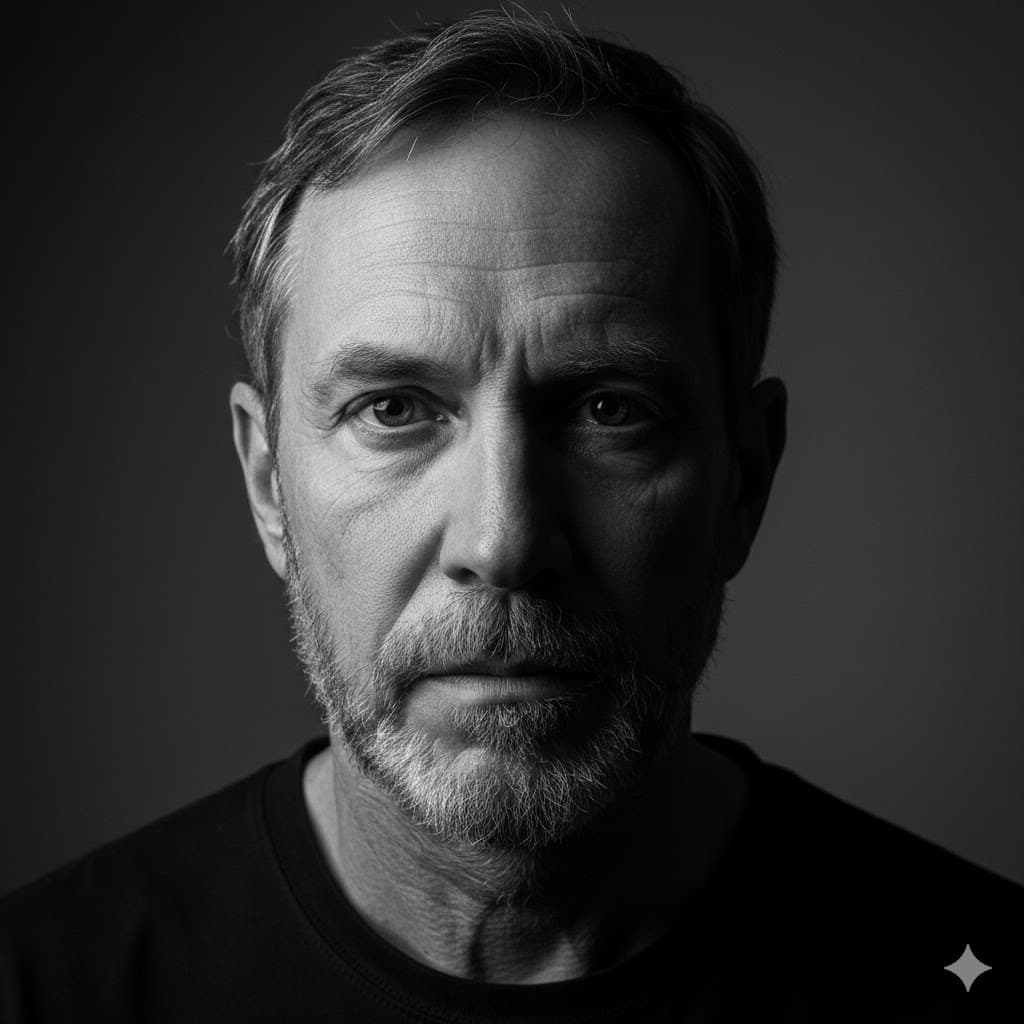

Split lighting, divides the face exactly in half into bright and dark, giving the impression of two different faces
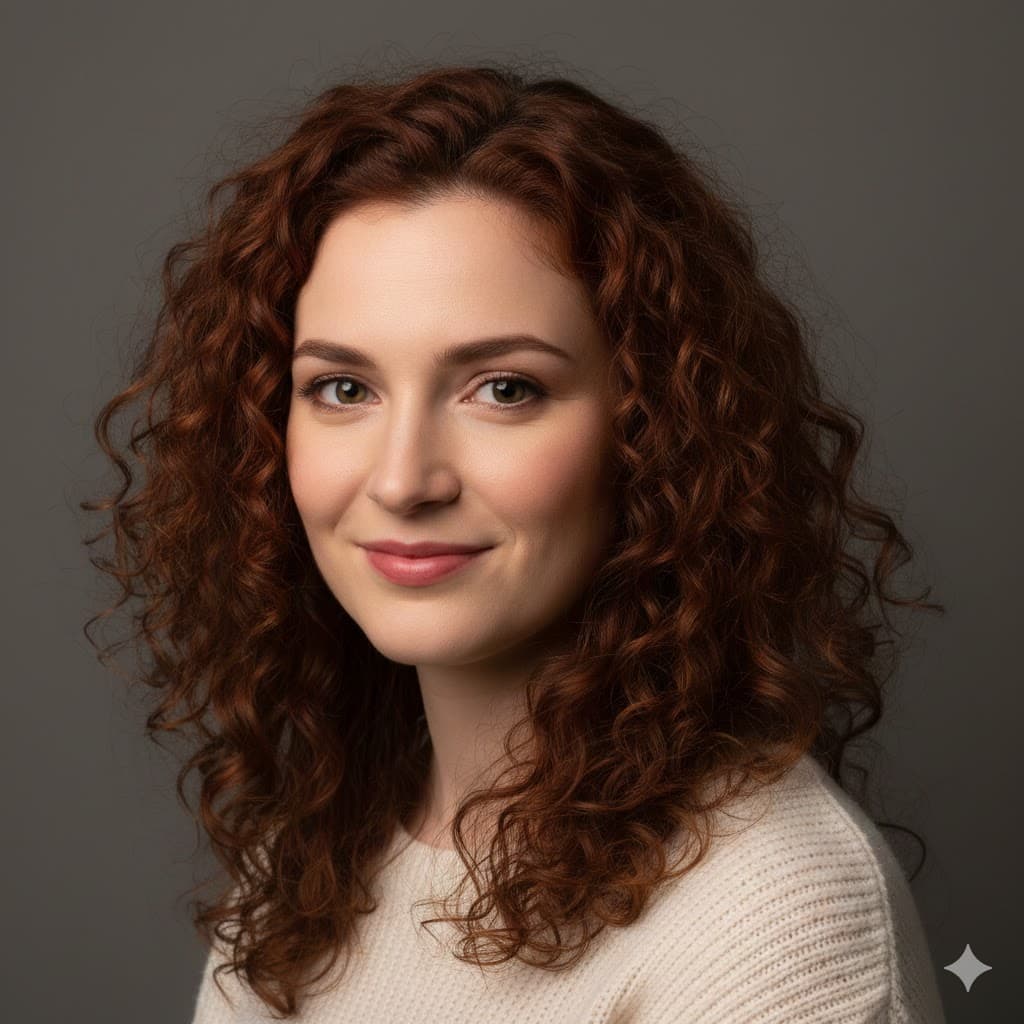

Loop lighting, the most standard and common portrait lighting that creates a small loop-shaped shadow next to the nose
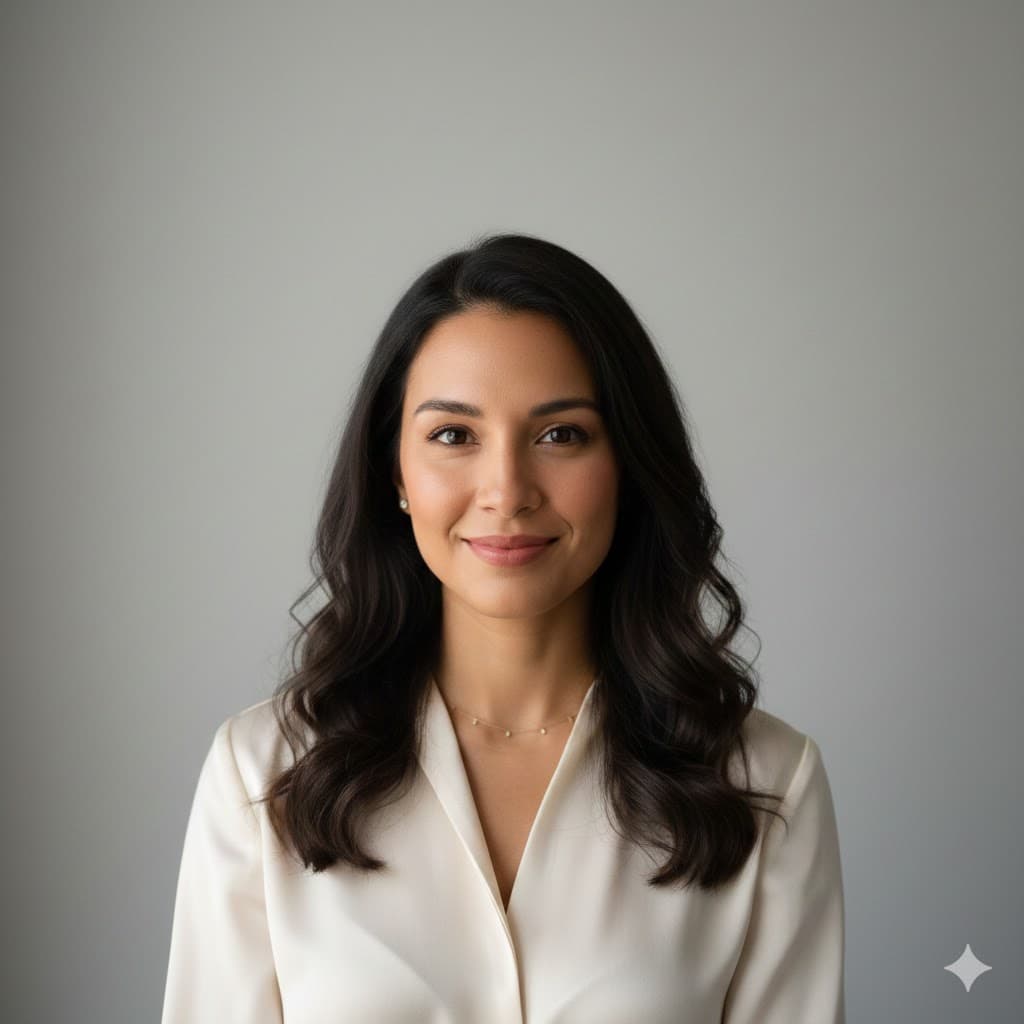

Broad lighting, brightly illuminates the wider side facing the camera, making the face look wider
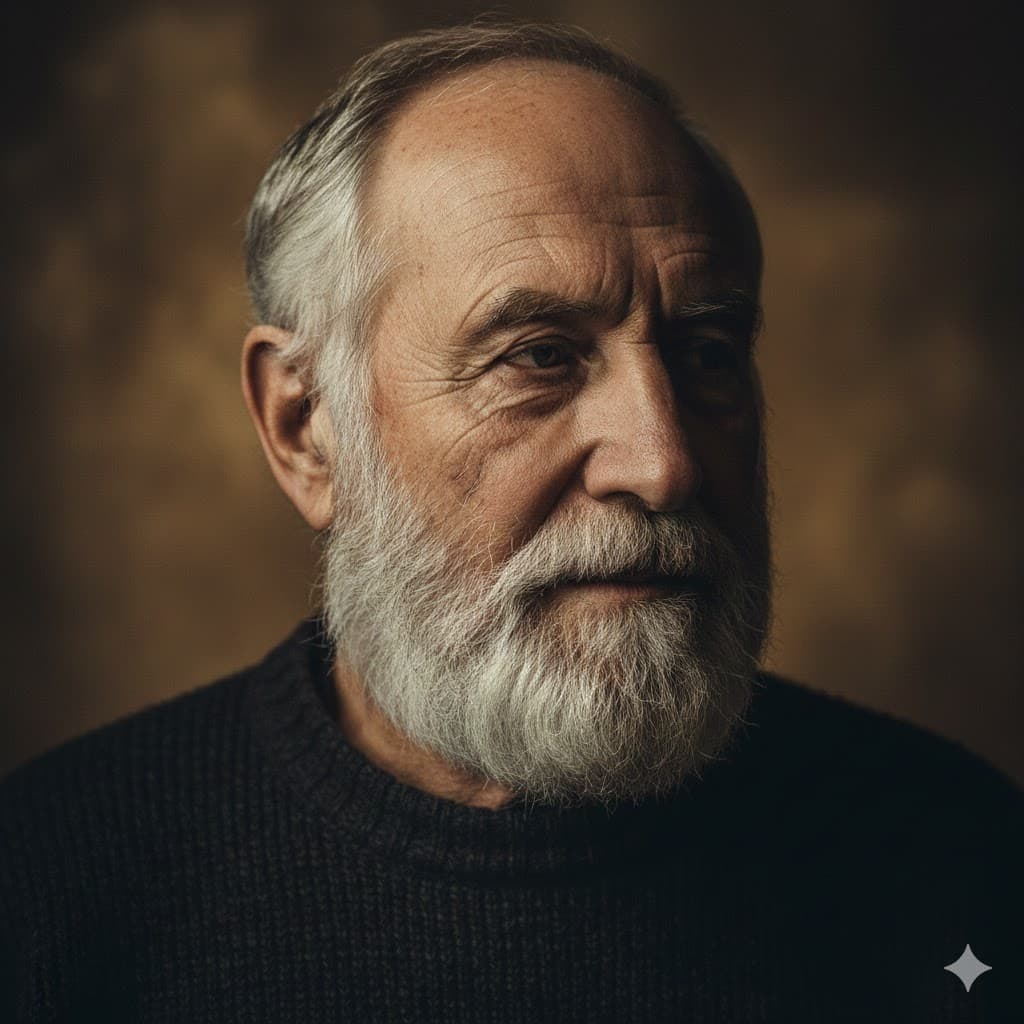

Short lighting, brightly illuminates the narrower side opposite the camera, making the face look slimmer and more three-dimensional
Environmental and Special Rendering Effects
Advanced techniques that add a sense of space and realism.
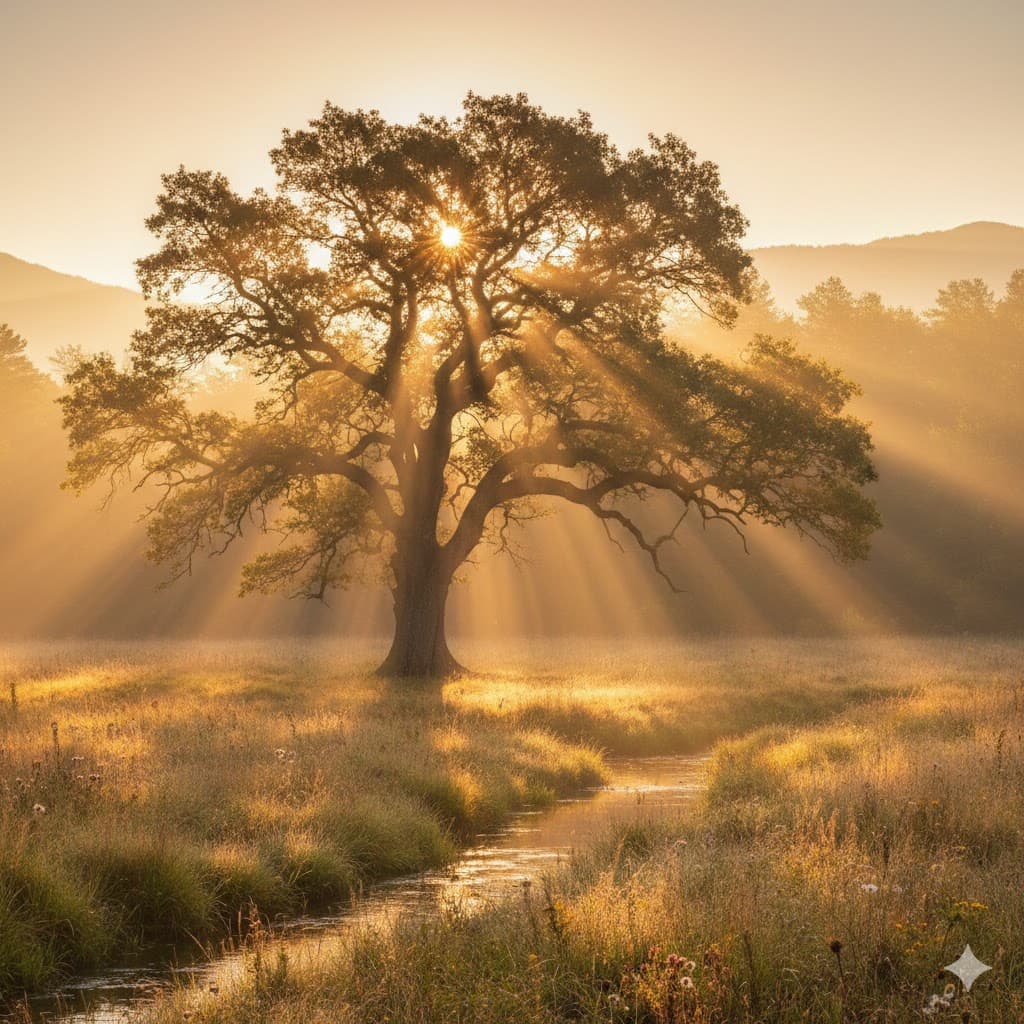

Volumetric lighting, a visible beam of light cutting through fog or dust, giving a sacred and majestic feeling

Global illumination, realistic 3D lighting where light bounces off walls or floors to gently fill the entire space
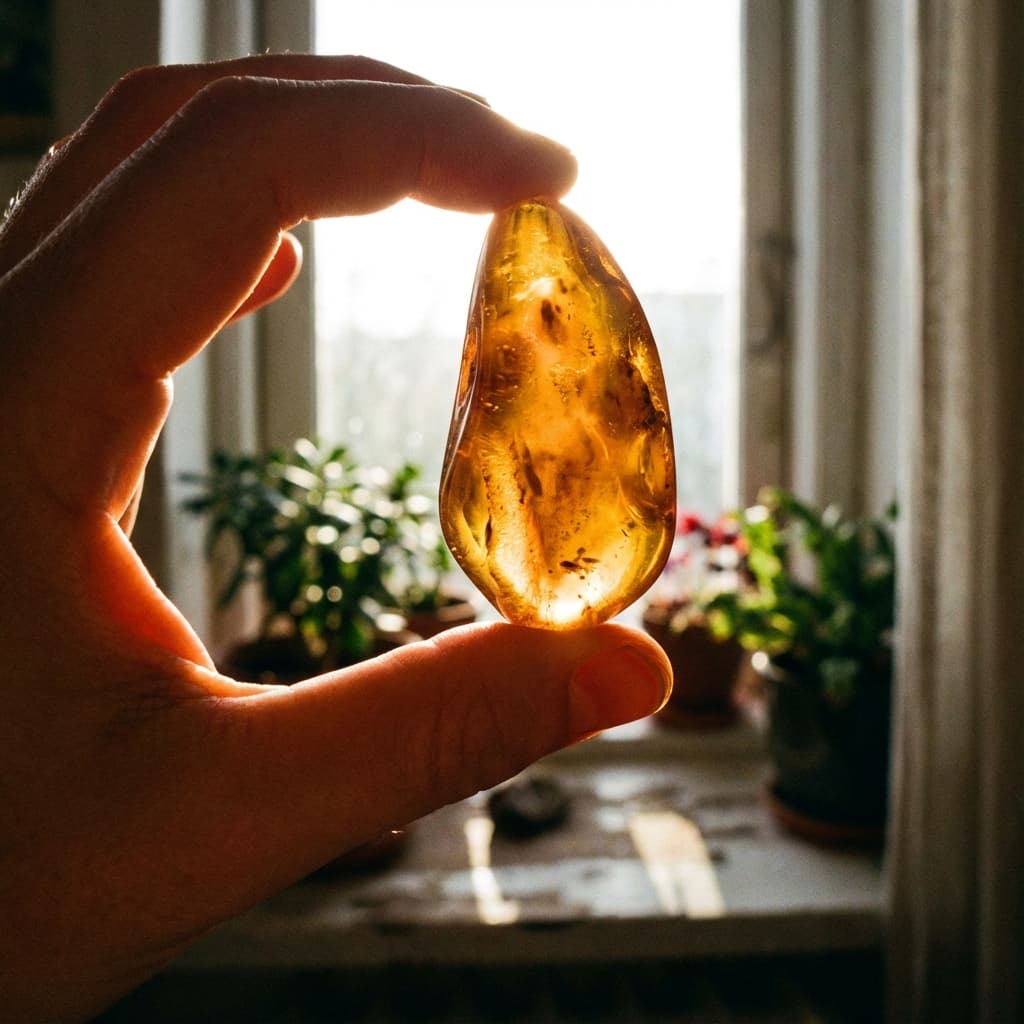

Subsurface scattering, light passing through skin, leaves, or jelly to create a reddish, translucent effect as if the inside is glowing
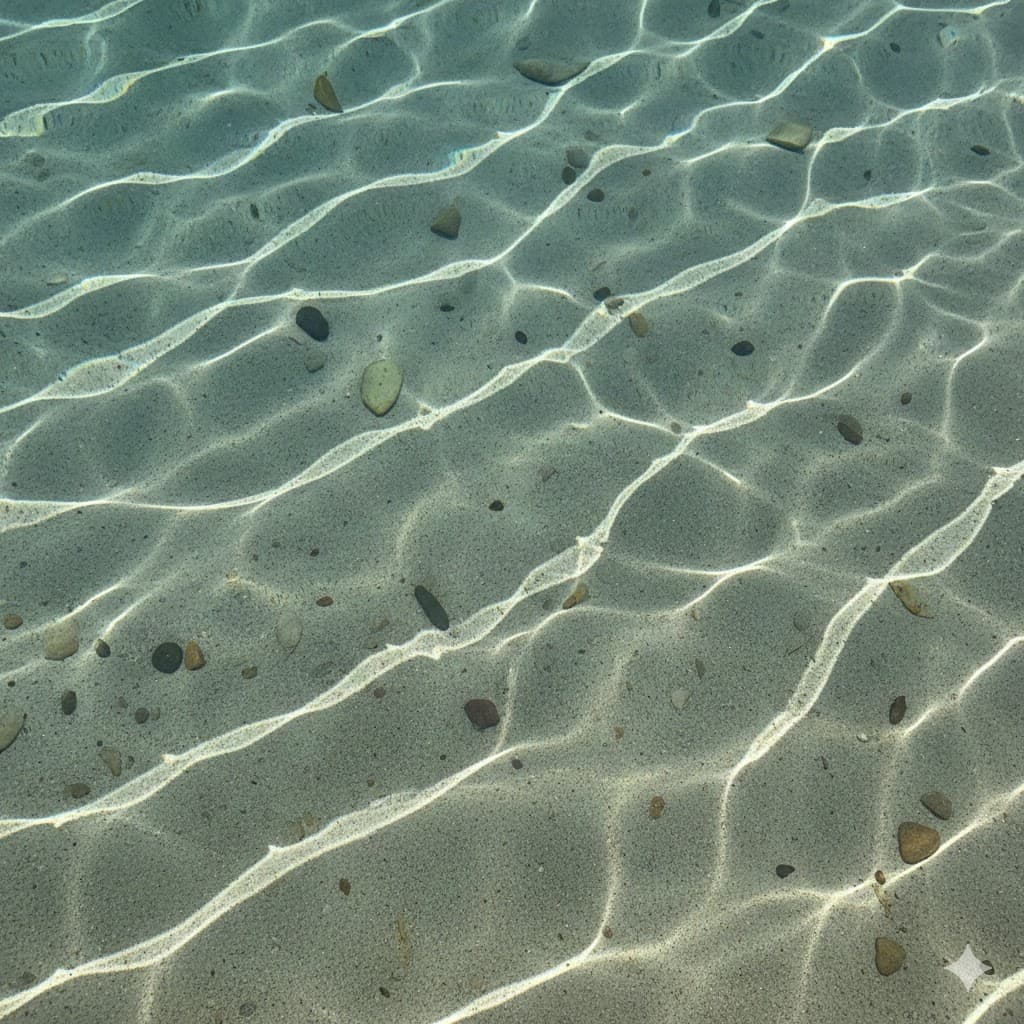

Caustics, shimmering mesh patterns of light created by refraction on a glass of water or the bottom of a swimming pool
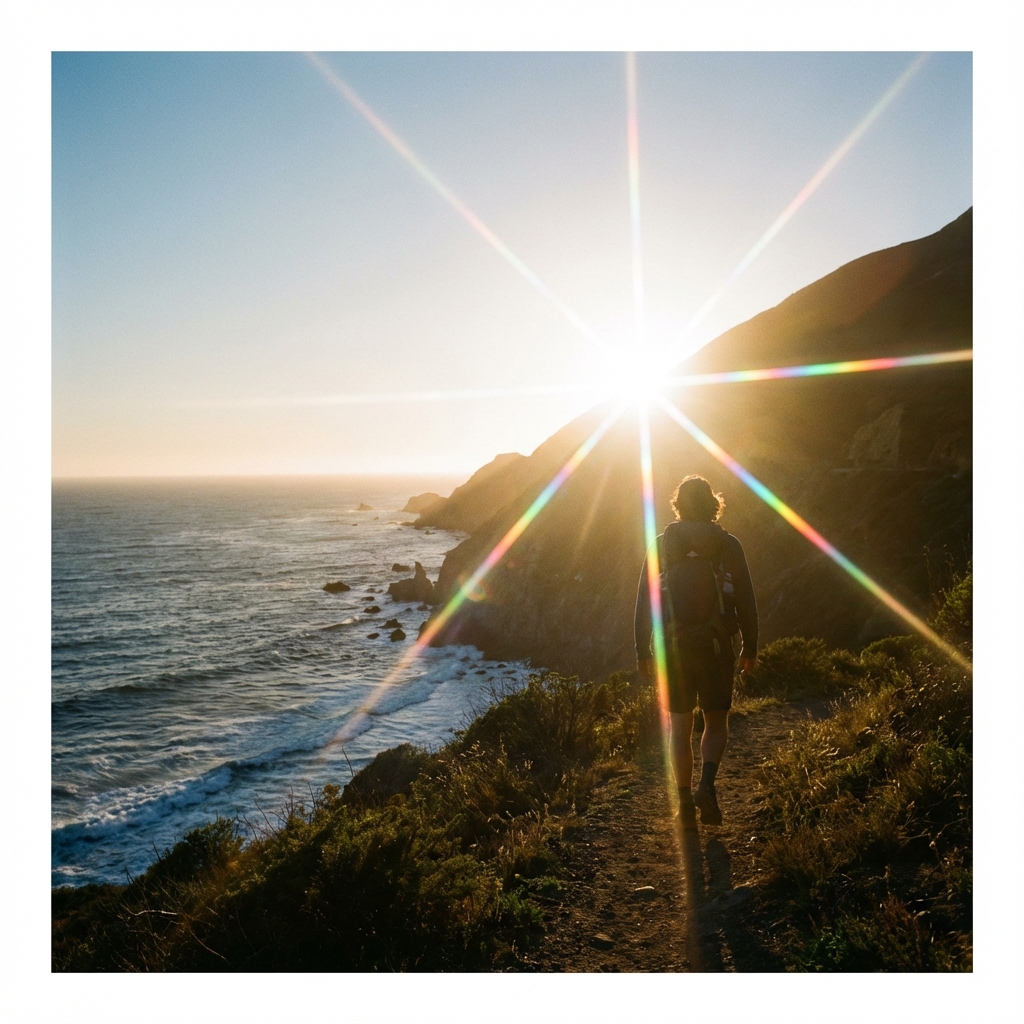

Lens flare, hexagonal light orbs that appear on the lens when facing a strong light source, giving a cinematic feel
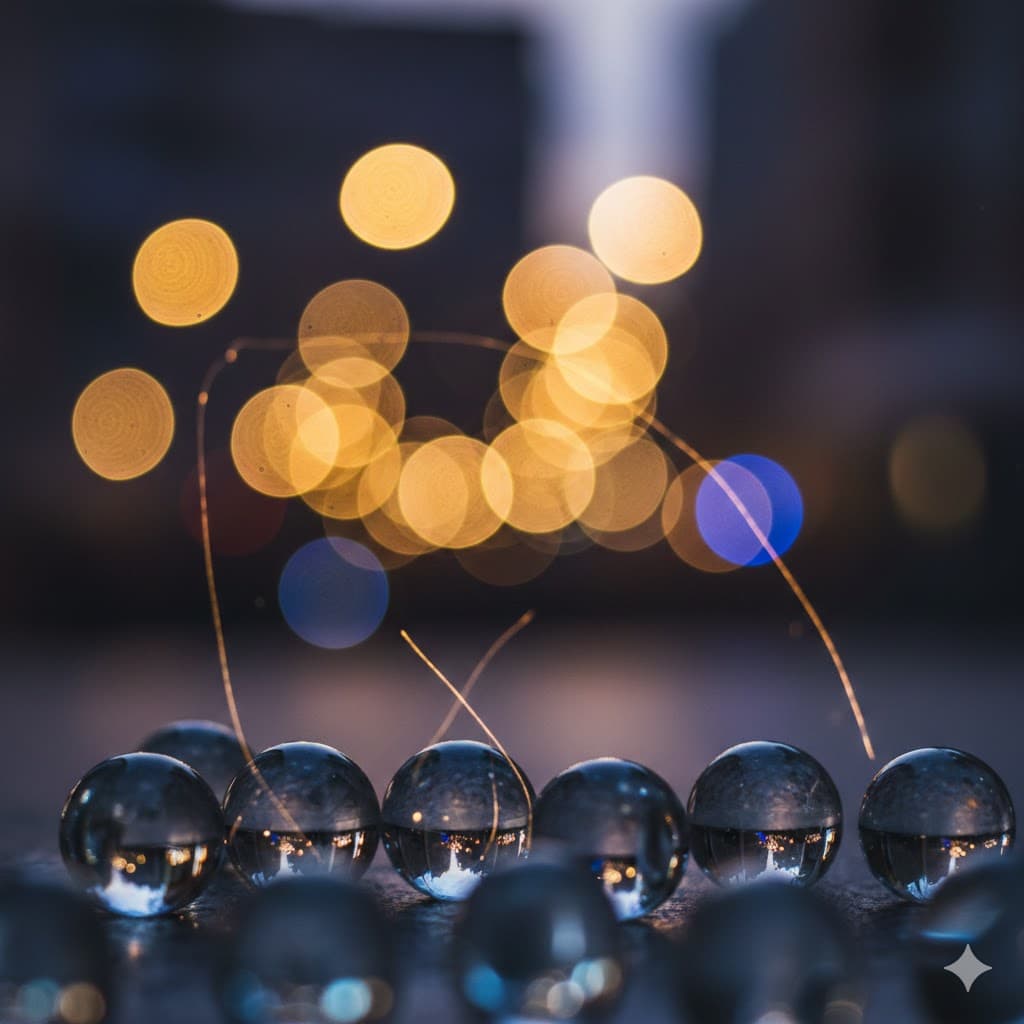

Bokeh, out-of-focus background lights forming soft, round blobs
Ambient occlusion, emphasizes the subtle, dense shadows that form in tight corners to bring out detail